Seznamy Classical Solar System Atomic Model Čerstvé
Seznamy Classical Solar System Atomic Model Čerstvé. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …
Tady Rutherford Model Experiment Observation Limitation
The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.
The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913... The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913... Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3)... Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.
Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results... Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model... Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.
The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets)... . He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model... The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode... Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results... He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). .. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode... He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. . The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913... Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3)... Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.
Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3)... It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …
He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode... He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.
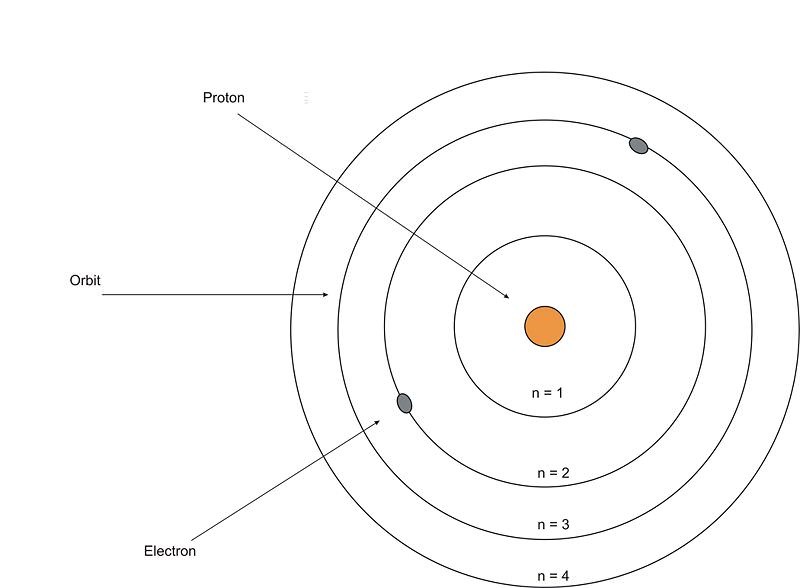
Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. . He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets)... Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets)... He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.
He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets)... The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode... The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode... Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.
It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus ….. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus ….. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields... Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus ….. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus …

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913... He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model... He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).
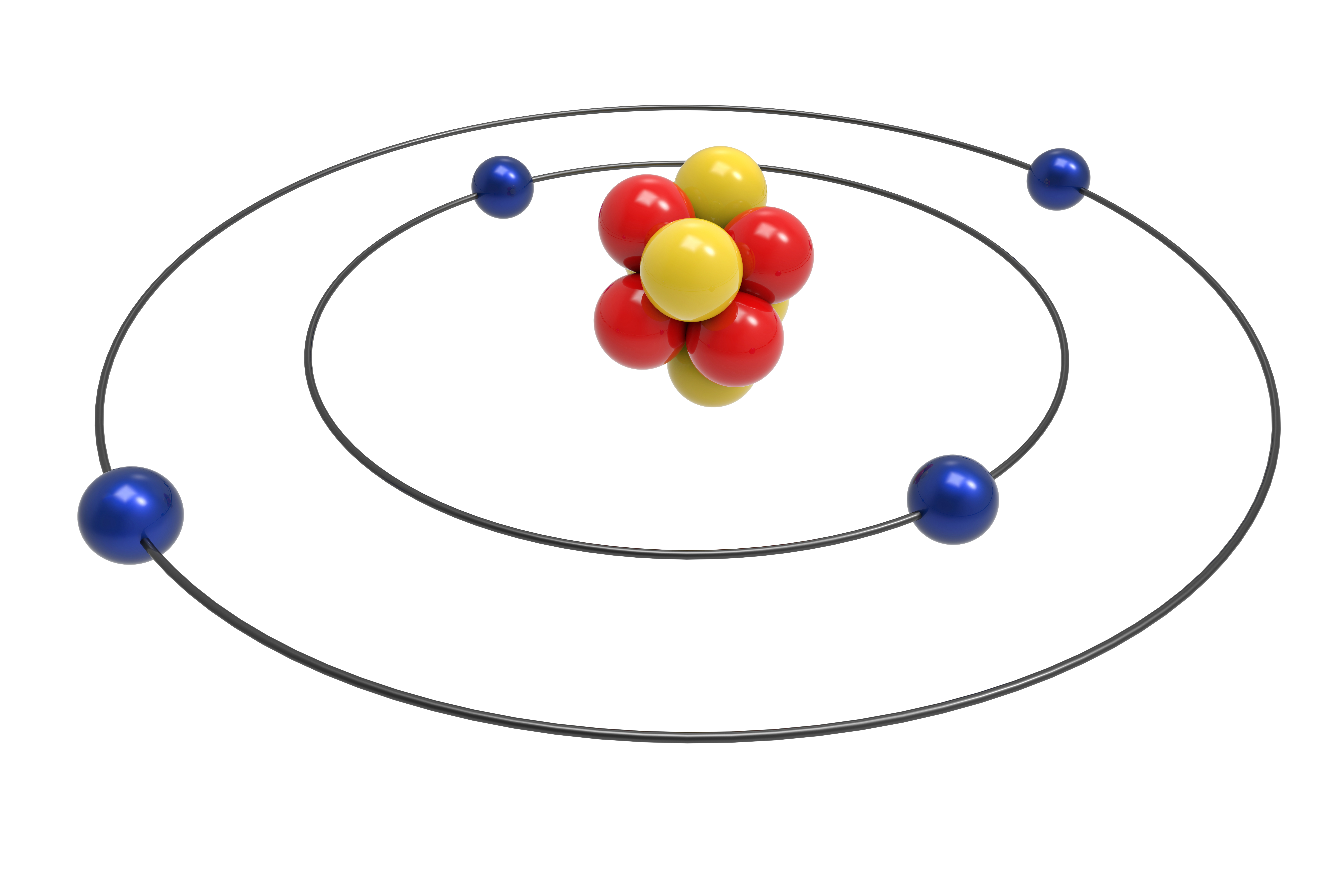
Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). . Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). .. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. .. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets)... The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.
He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode... Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model... The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus.
Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets)... The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). . He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets).

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. He realized that certain colors of light were given off when elements were exposed to flame or electric fields. It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.
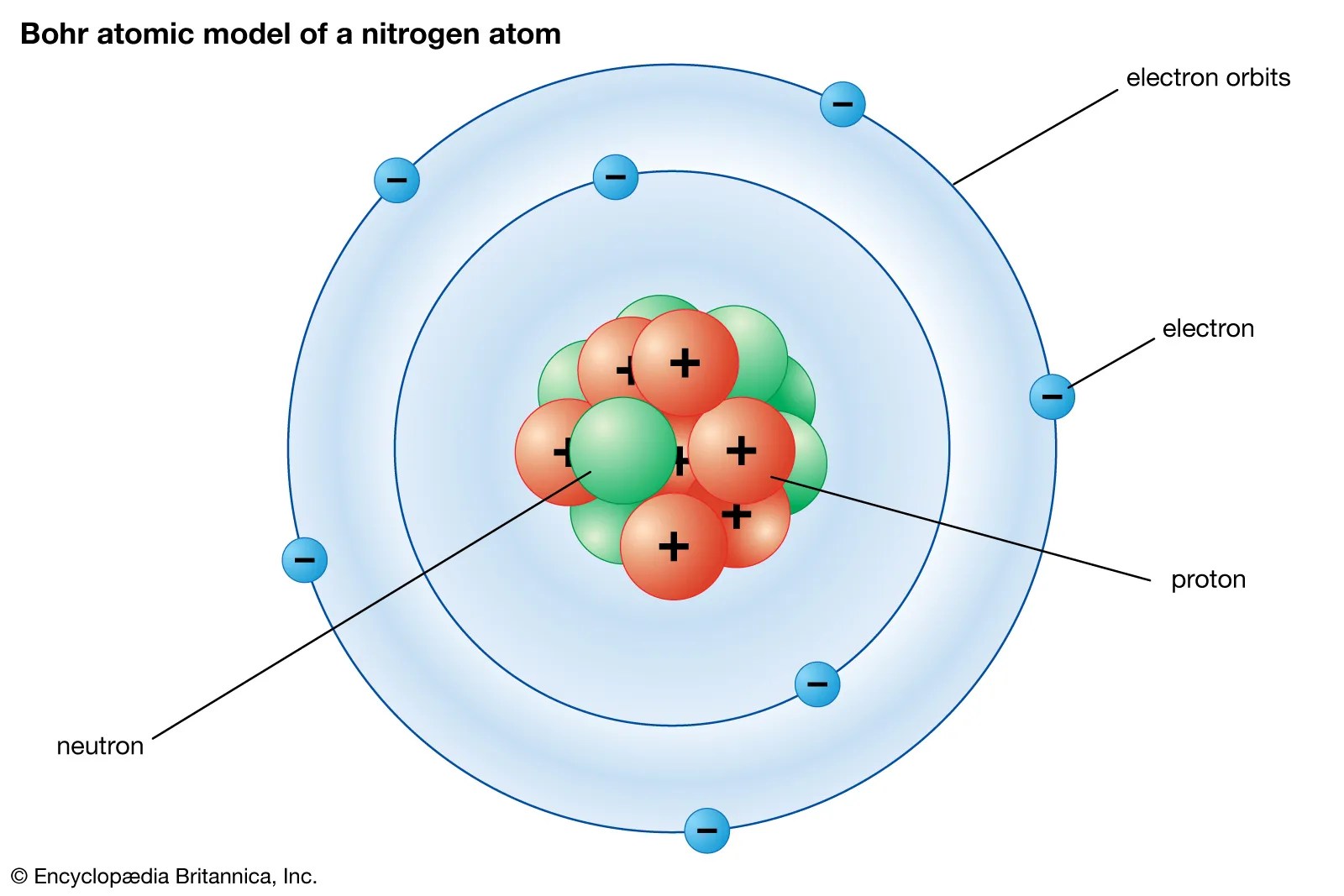
Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model.. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).

He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results.

It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode.. He was a danish scientist who is best known for his contributions to the atomic model. Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913.

Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). The solar system model describes an atom as a central massive positive entity (the nucleus/sun) and, orbiting around it, the negative entities (the electrons/planets). Neils bohr came up the solar system model of the atom in 1913. Thomson's currant bun model of the atom, in which positive charge was spread thinly over the whole atom, hadn't a hope of explaining the results. The problem with this is that the electrons are charged particles and moving around in a circle they have centripetal acceleration (even if they move with constant velocity in modulus … It shows that the negatively charged electron is attracted to the positively charged proton and so eventually the electron revolving around the nucleus is pulled into the center and the wholething will explode. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3). He was the first to realize that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus. Rutherford's new model instead, in 1911, rutherford cooked up a new model of the atom in which all of the positive charge is crammed inside a tiny, massive nucleus about ten thousand times smaller than the atom as a whole (fig 3).